Research Article Structure#
In this section, we will review the structure of a published research article. While the structure may vary slightly across journals, the general framework is consistent.
To access a published article, consider the following options:
If the article is open access, it can be downloaded directly from the publisher’s website.
For non-open-access articles, use your college library’s resources to access them.
Authors often share their articles on their personal websites.
You can reach out to authors via platforms like ResearchGate, a social networking site for sharing research papers, asking questions, and exchanging ideas.
Some articles may also be available on arXiv, an open-access archive for preprints.
We will use the following paper as an example to explore the structure in this section:
A stock time series forecasting approach incorporating candlestick patterns and sequence similarity.
Article Information Page#
The first page of a article typically contains the following information:
Publisher of the journal
Name of the journal
Publishing year and volume of the article
Title of the article
Author information, including affiliations
Keywords
Abstract

Structure of a Research Article#
In general, a research paper consists of the following parts:
Keywords
Abstract
Introduction
Literature Review
Methodology
Experiments, Results, and Discussions
Conclusions
References
Keywords#
These are the words and phrases that provide information about the topic and focus of the paper.
Keywords help readers and search engines identify the article’s subject matter.
Depending on the journal guidelines, 5-7 keywords are typically chosen to best represent the content of the paper.
Abstracts#
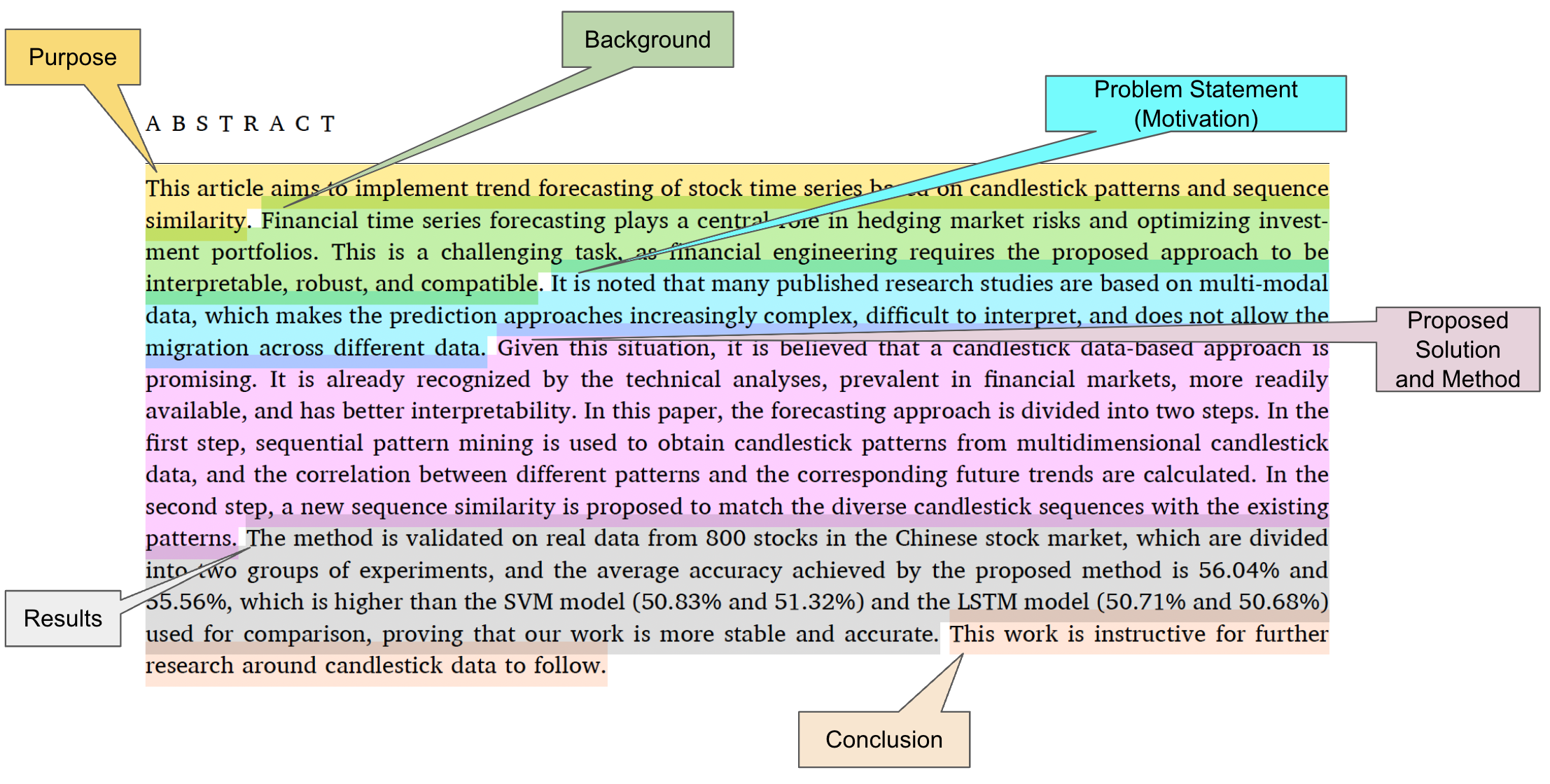
It is the brief summary of the whole paper which typically consists of following parts:
Purpose
Background (General Information)
Problem Statement (Motivation)
Proposed Method
Results
Conclusion
Introduction#
The Introduction section serves as the starting point of the research paper and typically includes:
Background Information: Provides context for the study, often referencing related works and previously conducted research.
Research Problem: Clearly states the problem being addressed, emphasizing its importance and the motivation behind the study.
Objectives and Significance: Outlines the goals of the research and its potential contributions or impact.
Organization of the Paper: The final paragraph usually provides an overview of the structure of the article, describing each section.
Literature Review#
The Literature Review provides an overview of existing research on the topic and includes two key components:
Evaluation of Previous Research: Summarizes and critically assesses past studies related to the subject.
Identification of Gaps: Highlights gaps in the existing knowledge or unresolved questions that the current study aims to address.
This section also serves as a valuable resource for readers by guiding them to useful references and sources related to the topic. Survey papers, in particular, are excellent for understanding how the subject has been explored from various perspectives.
Methodology#
The Methodology and Experiments, Results, and Discussions sections form the core components of the research work. Together, these sections provide the technical and analytical backbone of the paper.
The Methodology section provides a detailed description of the procedures, techniques, and tools used to conduct the research. It also includes definitions of fey terms and concepts that will be used throughout the paper are defined here.
This part is a crucial component of the paper, often containing many technical details. A good practice for understanding this section is to start with skimming and gradually delve into the specifics with repeated readings.
Additionally, the methodology should be designed to support reproducibility, allowing other researchers to replicate the study.
Experiments, Results, and Discussions#
This section provides a comprehensive account of the research process and findings, including:
Experiment Details:
Description of the experiments, including steps like data preparation (e.g., importing, cleaning, normalizing).
Setup and application of methods to the prepared data.
Analysis and Comparisons:
Detailed analyses of the results, including the performance of baseline methods to compare and validate the proposed approach.
Demonstration of the efficiency of the current method in relation to previous works.
Presentation of Findings:
Results are presented using visual aids like graphs, tables, and charts for clarity and comparison with prior research.
Interpretation and Implications:
Explanation of the results, their significance, and what they imply for the field or potential applications.
Conclusions#
The Conclusions section provides a concise summary of the study, including:
Methodology Recap: A brief overview of the methods used in the research.
Main Findings and Results: Highlights of the key outcomes and their relevance.
Additionally, it includes:
Significance of the Results: A discussion of the impact and implications of the findings.
Recommendations or Future Research Directions: Suggestions for further exploration or unanswered questions in the field.
This section can be a valuable resource for identifying potential research questions or areas to explore further.
References#
It is the list of the sources used throughout the article including published research papers, books, datasets..etc
The References section provides a list of all the sources cited throughout the article. These can include:
Published research papers
Books
Datasets
It allows readers to explore the background material or verify the sources used in the study.
This section follows specific formatting styles that vary in terms of the order and presentation of elements such as author names, publication dates, and volumes.
Different journals adopt distinct reference styles, such as APA, MLA, Chicago, or IEEE.
The formatting style includes rules for how to list authors, organize publication details, and structure citations.
Journals specify their required style in their submission guidelines, and authors must adhere to these standards for proper formatting.
